Jaw Muscle Injection (TMJ)
Due to the complex and dense anatomy of the region, blind injection of the temporalis may result in an unintentional injury.
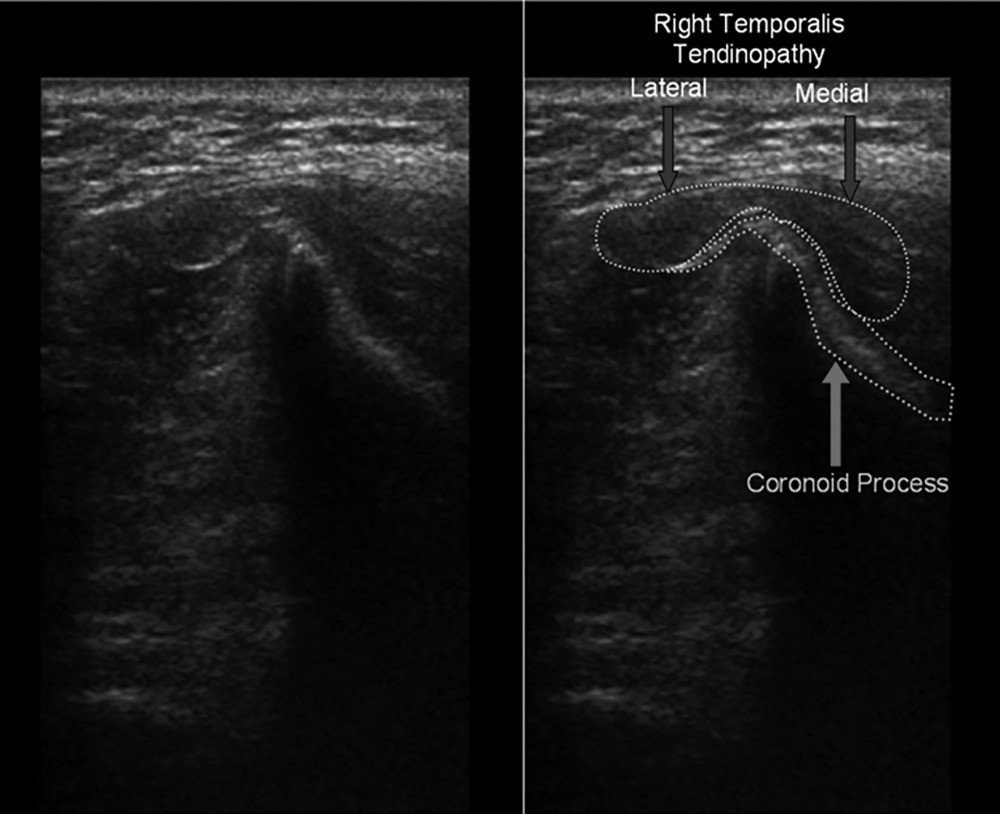
Ultrasound‐guided injection of the temporalis tendon is based on visualization of the temporalis muscle, temporalis tendon, and coronoid process.
Which ultrasound scanner do doctors use for Jaw muscle injections?
The doctors needs a 10 to 14 MHz SIFULTRAS-3.5 Linear Ultrasound Scanner.
To visualize the temporalis tendon, the transducer is best placed inferior to the anterior aspect of the zygomatic arch, unlike the temporomandibular joint, where it is placed over the articular surface of the mandibular condyle
When the mandible is in the closed‐mouth position, the coronoid process is anatomically underneath the zygomatic arch and is therefore inaccessible. Opening the mouth fully will bring the coronoid process out from under the arch to be visualized. The temporalis tendon insertion can be visualized in the sagittal plane (long axis) in both the open‐ and closed‐mouth positions but is best visualized in the axial plane (short axis) in the open‐mouth projection, which is optimal for injection.
Once the musculotendinous junction is visualized, the needle is then directed to the medial insertion imaging is required to locate the distal temporalis tendon and to confirm the presence of temporal tendinosis. The ultrasound‐guided anatomic technique ensures correct injection of the direct temporalis tendon and prevents potential injury of any of the closely adjacent structures. This technique is practical for both the diagnosis and treatment of patients presenting with chronic facial pain syndromes.
This way, the Anesthesiologist can view the mandibular condyle on the screen.
References: Ultrasound‐Guided Injection of the Temporalis Tendon: A Novel Technique
[launchpad_feedback]
Although the information we provide is used but doctors, radiologists, medical staff to perform their procedures, clinical applications, the Information contained in this article is for consideration only. We can’t be responsible for misuse of the device nor for the device suitability with each clinical application or procedure mentioned in this article.
Doctors, radiologists or medical staff must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each ultrasound scanner device.